Expand the Scope of Automation Scanners Using Burp-Suite
Limitations of Automation Scanners
The market offers a range of security scanners, including HCL AppScan, Acunetix, and Netsparker, among others. However, it is observed that these types of automated scanners have some disadvantages, basically, these automated security scanners are not smart enough to understand the requirements of user input fields. sometimes they are not able to reach each and every function while spidering or crawling the applications. Because of these disadvantages, it is possible that we might have missed the vulnerabilities.
Actually, we can resolve these problems by exploring the entire application manually in automation scanners.
Suppose if we want to scan a single application with multiple tools then, we have to explore the entire application multiple times for each tool.
So our goal is to explore the entire application once manually and capture the traffic in burp-suite and then transfer the captured traffic from burp-suite to HCL AppScan or other automation tools for security scanning
About Burp-Suite
Burp-Suite is very popular in the hacking community because of the flexibility and high-level customization capabilities of the burp-suite. It allows users to modify and craft requests, intercept and modify responses, and perform in-depth manual testing.
The burp-suite proxy tool connects to the browser, so whatever we explore or trigger the functionality of target application in the browser, it will be captured by the burp-suite tool. Burp-Suite can store the request and response with proper user inputs and application flow.
Since our goal is to explore the entire application once manually and capture the traffic in burp-suite and then transfer the captured traffic from burp suite to HCL AppScan or other proxy tools, we will use Burp-Suite Upstream Functionality here.
Burp-Suite Upstream Tool
Upstream Functionality is used to route the traffic form Burp-suite to other proxy tools or machine. The Burp Suite Upstream Setting refers to a feature within the Burp Suite tool that allows users to configure upstream proxies. Upstream proxies act as intermediaries between the client and the server, forwarding requests from the client to the server and vice versa.
Burp-Suite Repeater Tool
Repeater allows you to modify any part of an HTTP request, such as headers, parameters, cookies, or the request body. You can then resend the modified request to the target server and observe the response. This functionality is helpful for testing different input values, parameters, or headers to identify vulnerabilities or to understand how the application responds to specific inputs.
Setup
The scenario for the setup is as follows.
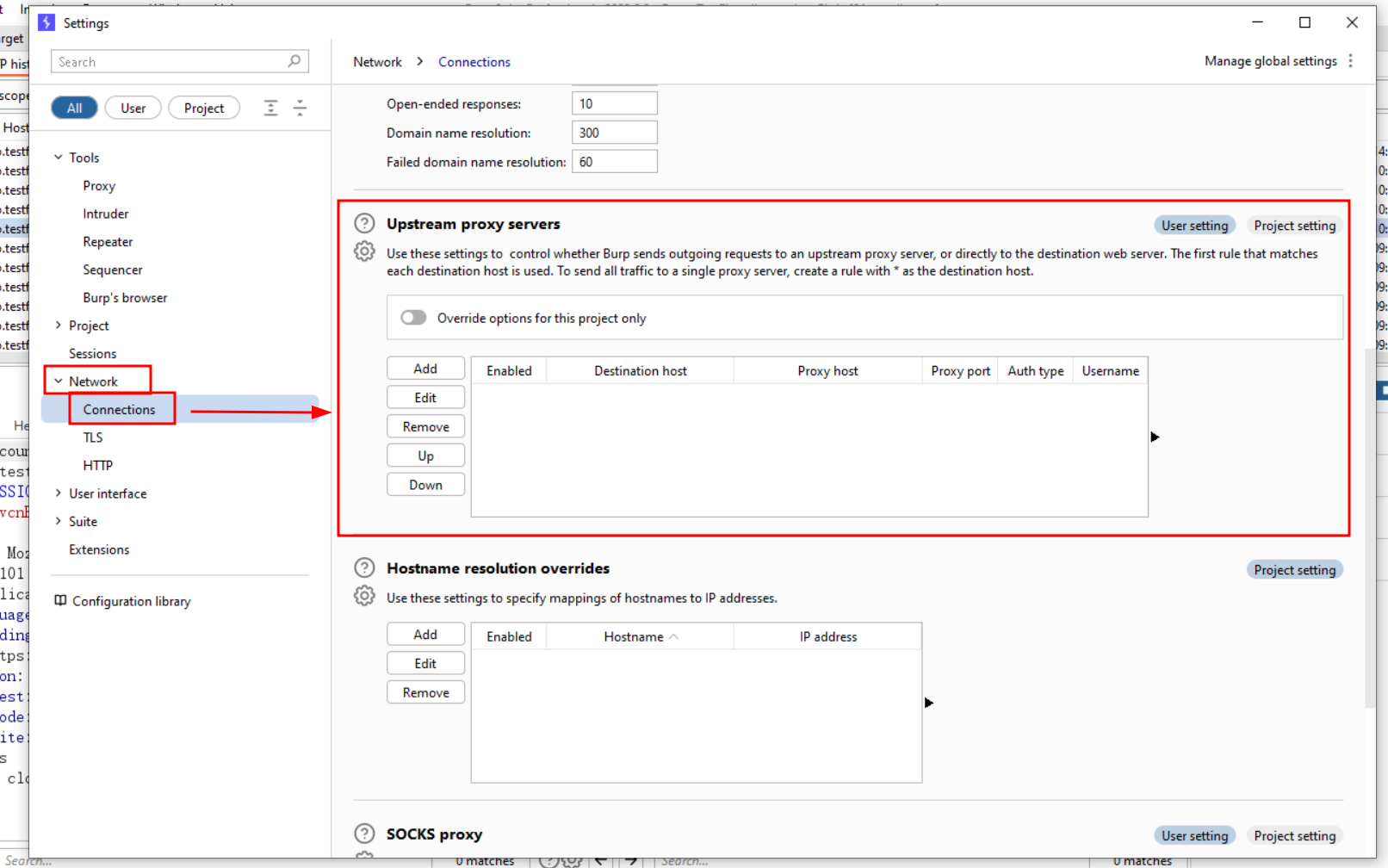
- Burp-suite will be the sender, so we will setup the “Upstream Proxy Server” in Burp-suite and
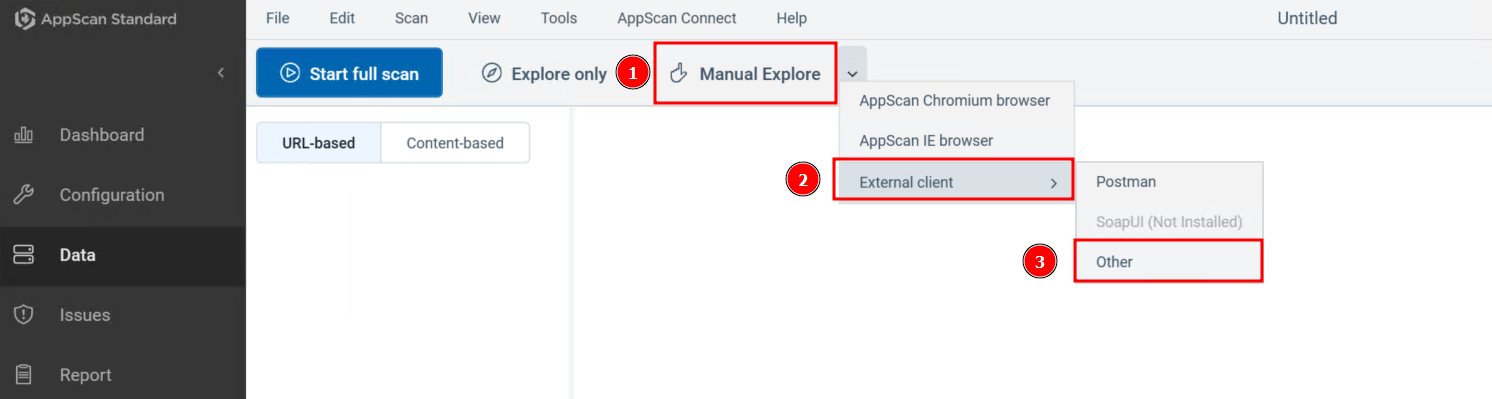
- HCL AppScan will be the receiver, so we will need to setup a Proxy Listener in HCL AppScan to record the traffic.
Step 1:
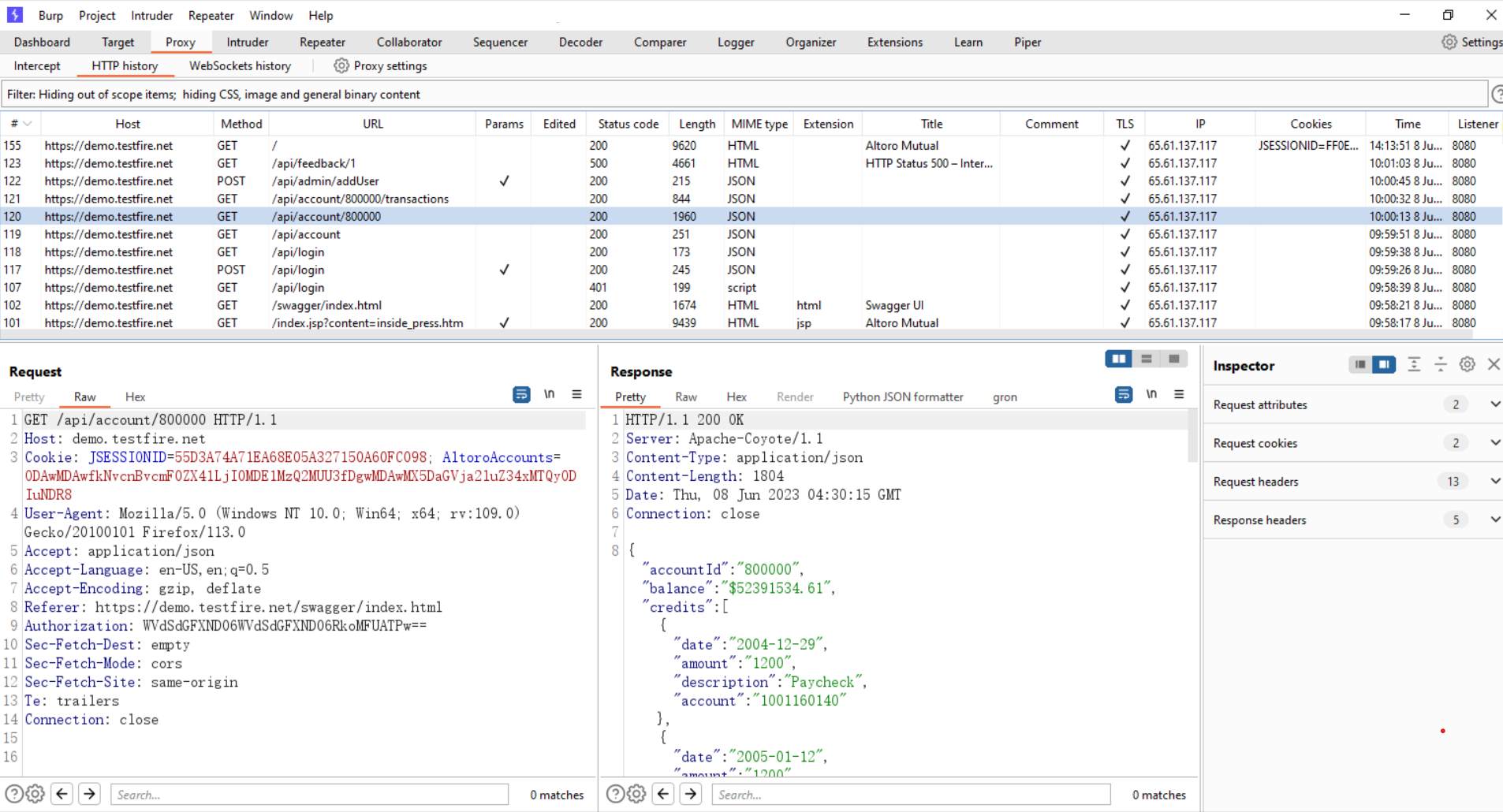
Explore the entire application in burp suite. trigger the each and every function of application with proper user inputs and flow.
In the following image, you can see that we have already explored the entire application https://demo.testfire.net
Step 2:
Set up a traffic listener in HCL Appscan to capture the traffic which will be sent from BurpSuite. 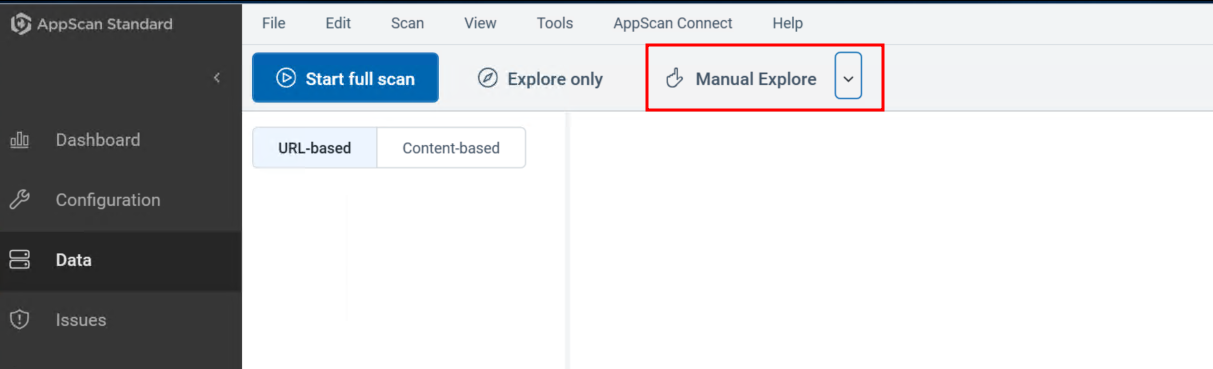
Step 3:
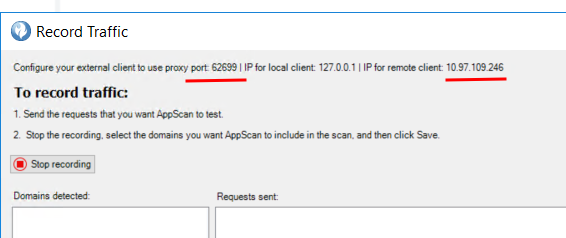
Successfully started the traffic listener to record the traffic in HCL Appscan. 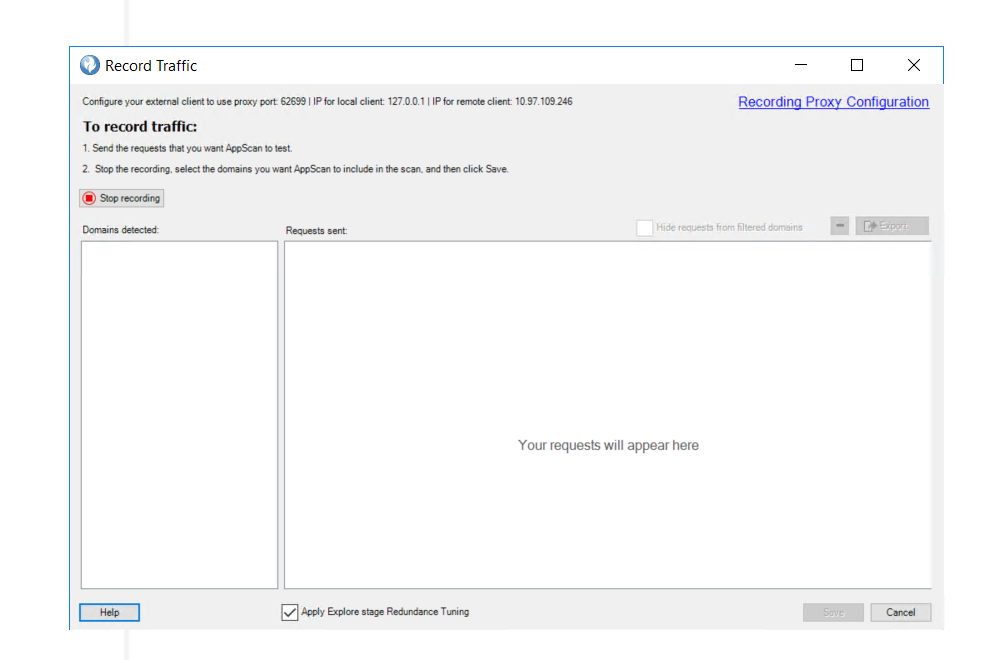
Step 4:
Once we get the details like IP address and Port number of HCL Appscan traffic listener, use those details in Burp-Suite upstream.
Step 5:
To add the details of the upstream proxy server, click on the “Add” button. 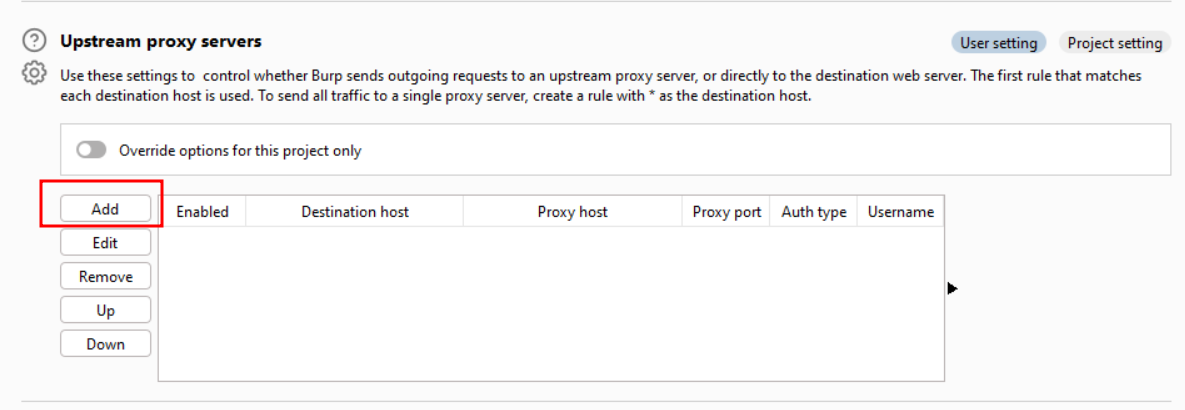
We get these below details from step 3 and step 4, once setup has been completed click on the Ok button 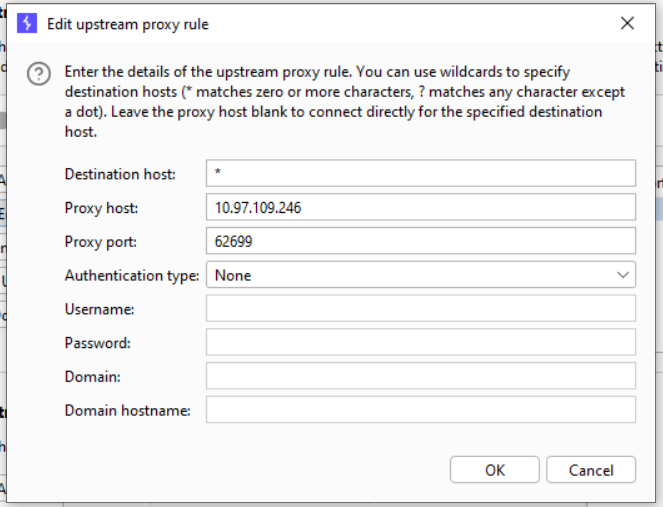
Step 6:
After setting up upstream, the next step is to choose the request that you wish to upstream toward the HCL AppScan.
You must send the request to the repeater once you have selected the request. 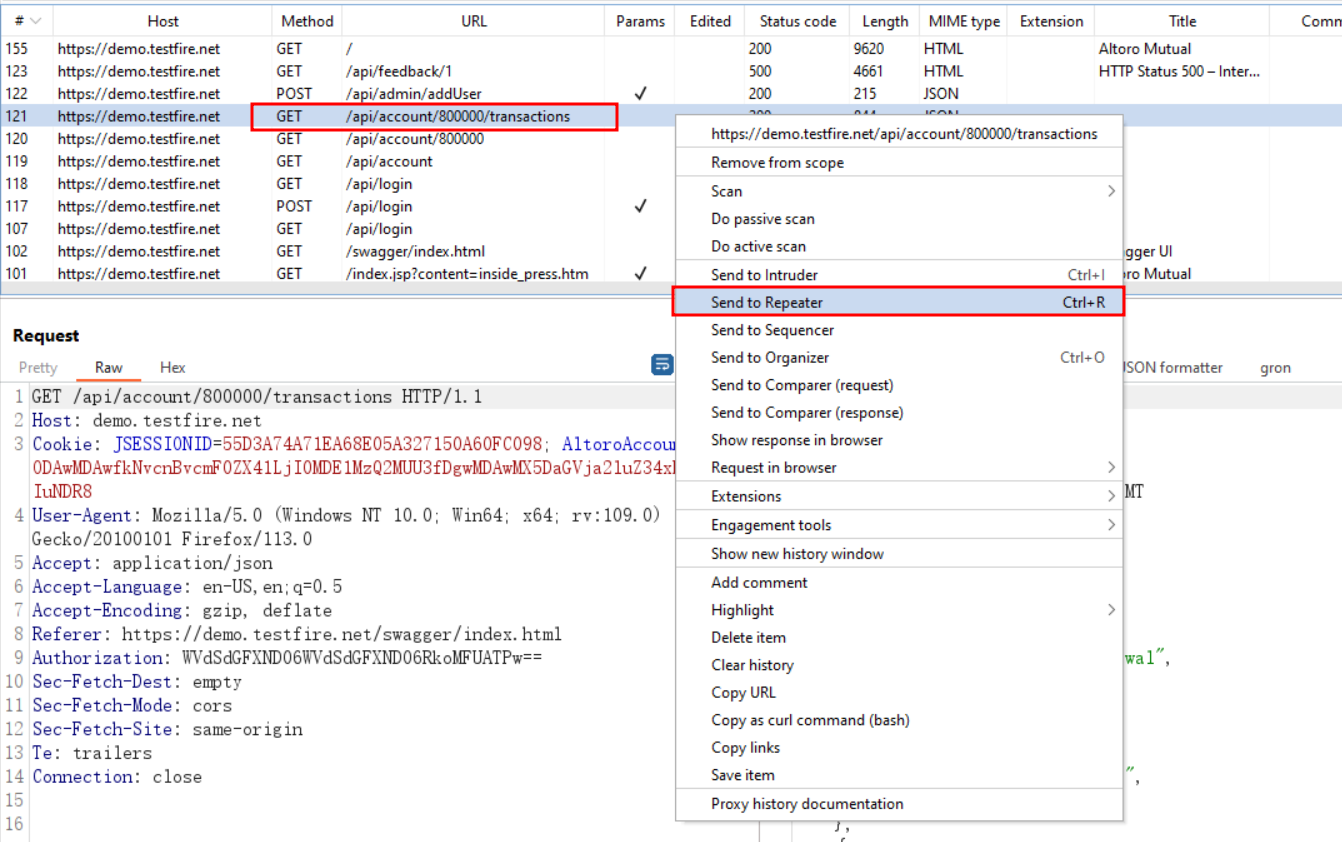
Step 7:
As soon as we click the send button of repeater, the request will be sent through the HCL Appscan to the server (Basically, once we click the send button,request will go upstream to HCL AppScan). 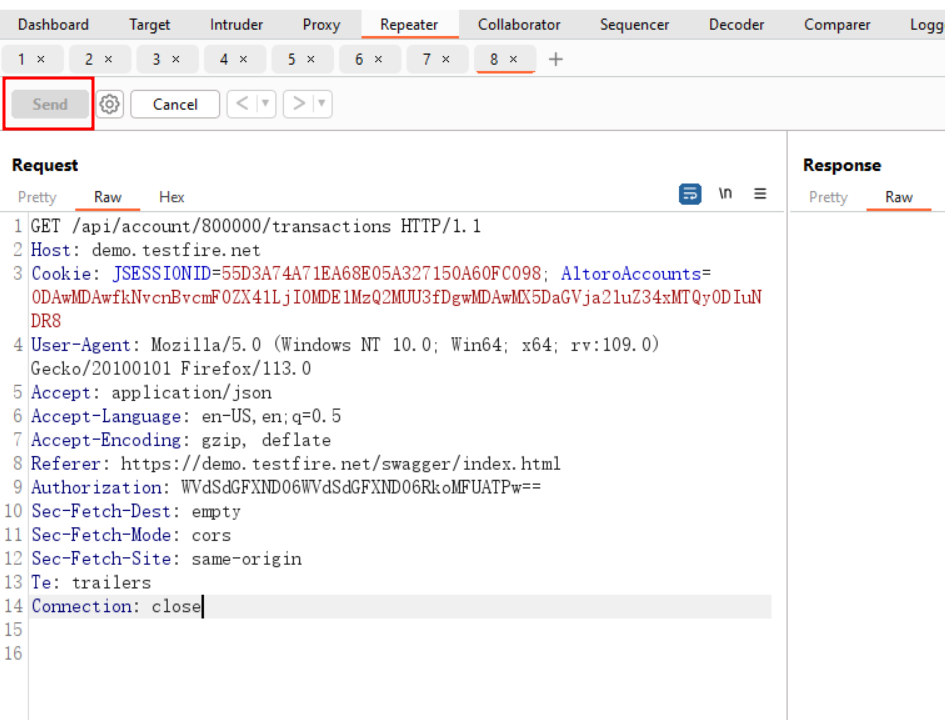
We are able to upstream the request as shown in the following image. 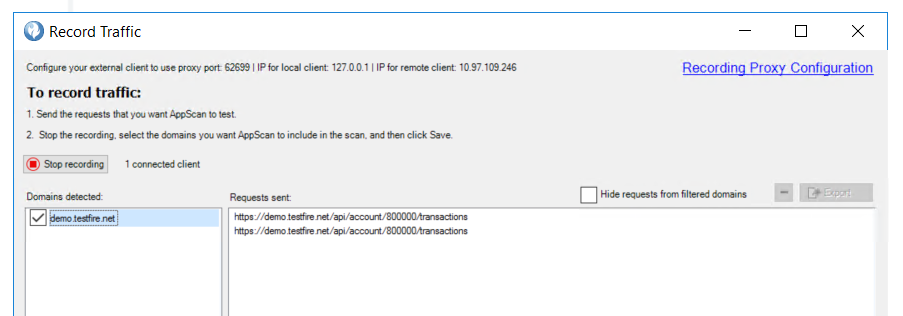
Step 8:
successfully able to upstream the 4 requests one by one using burp-suite repeater. 
However, the problem is that all requests must be re-executed or resent manually using the burp-suite repeater in order to upstream the request. Suppose if we want to upstream hundreds or thousands of requests, so we cannot repeat each request manually. In order to facilitate the upstreaming of requests, I develped the Burp Extender in Jython language. This extender allows for the repetition or re-execution of multiple requests with a single click.
Multi-Request-Repeater (Burp-Suite Extender)
https://github.com/IAmRoot0/Multi-Request-Repeater
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
import threading
from burp import IBurpExtender, IContextMenuFactory, IContextMenuInvocation
from javax.swing import JMenuItem
from threading import Thread
class BurpExtender(IBurpExtender, IContextMenuFactory):
def registerExtenderCallbacks(self, callbacks):
self._callbacks = callbacks
self._helpers = callbacks.getHelpers()
self._context = None
callbacks.setExtensionName("Multi-Request-Repeater")
callbacks.registerContextMenuFactory(self)
def createMenuItems(self, contextMenuInvocation):
self._context = contextMenuInvocation
menu_list = []
menu_list.append(JMenuItem("Repeat Selected Requests", actionPerformed=self.actionPerformed))
return menu_list
def actionPerformed(self, event):
selected_messages = self._context.getSelectedMessages()
timeout = 30000 # 30 seconds
for message in selected_messages:
# Send the message to the server
http_service = message.getHttpService()
request = message.getRequest()
thread = threading.Thread(target=self.send_request, args=(http_service, request, timeout))
thread.start()
def send_request(self, http_service, request, timeout):
response = None
try:
response = self._callbacks.makeHttpRequest(http_service, request, timeout)
except Exception as e:
print(e)
return response
Step 9:
Install the burp extension. Select multiple requests that you wish to upstream to HCL AppScan and click “Repeat Selected Requests”. 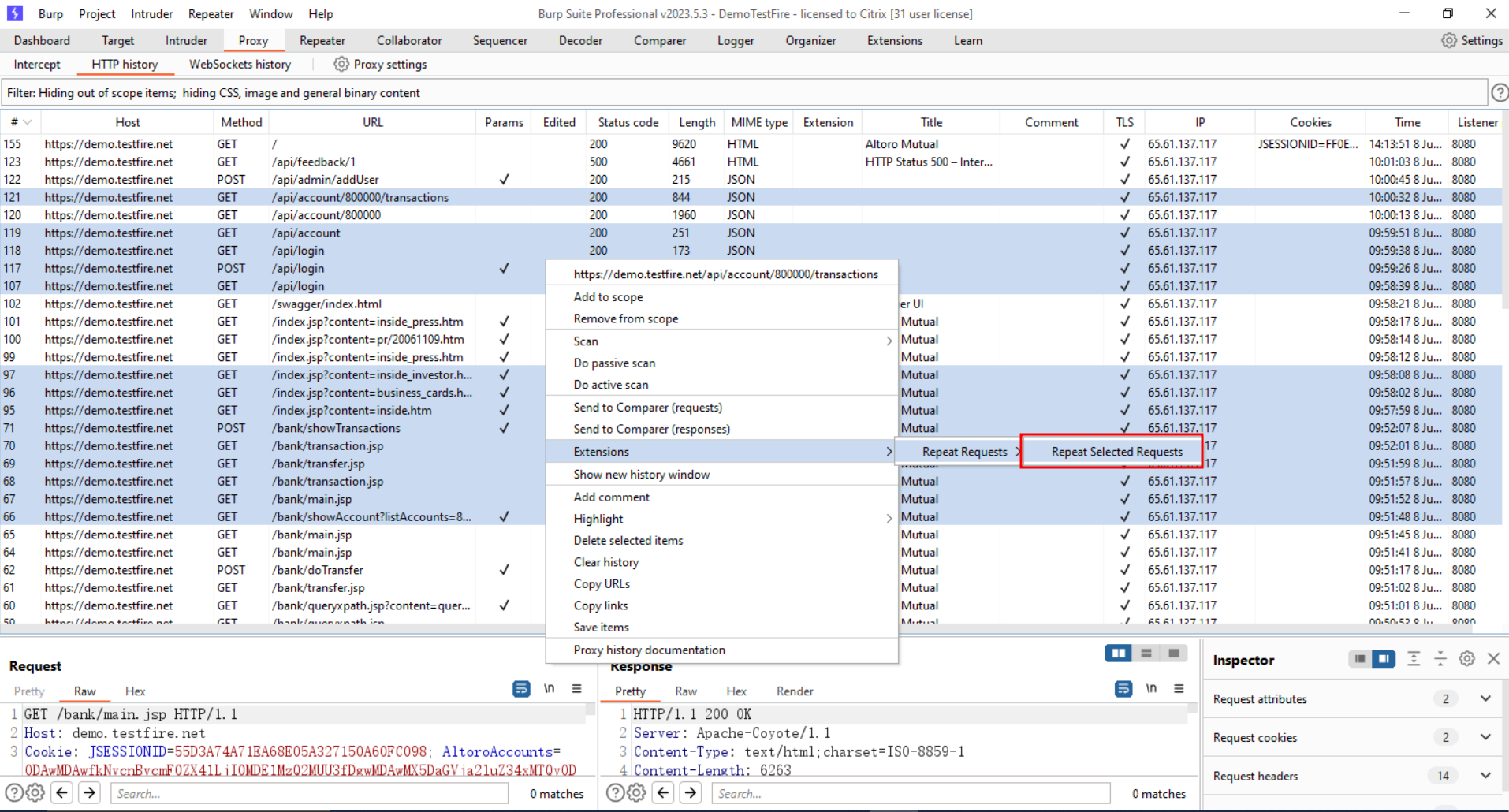
As you can see in below image, we are able to successfully upstream the traffic from burp-suite to HCL AppScan. 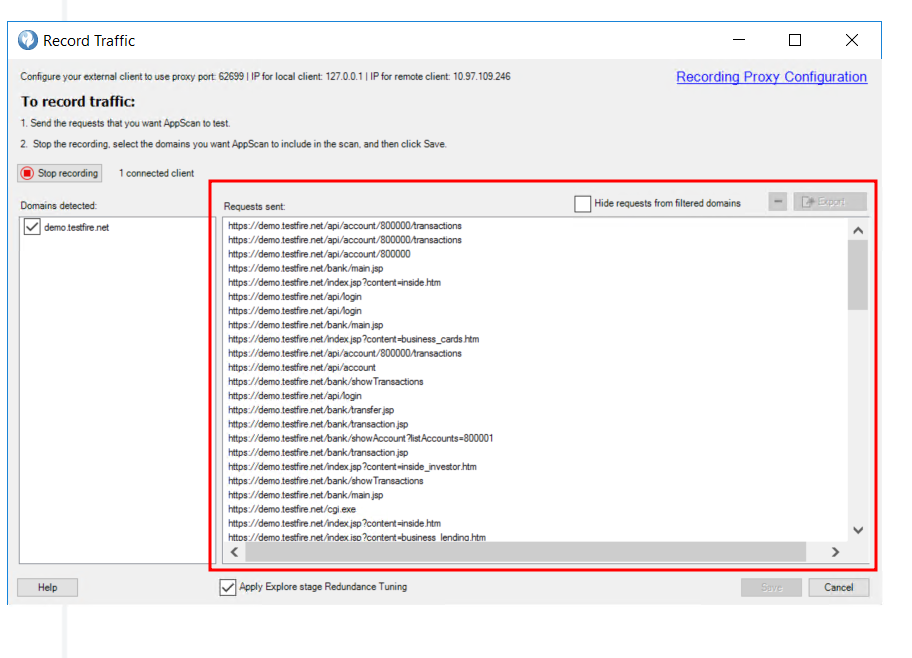
Step 10:
Stop the recording and then save the state and finally start the scan. 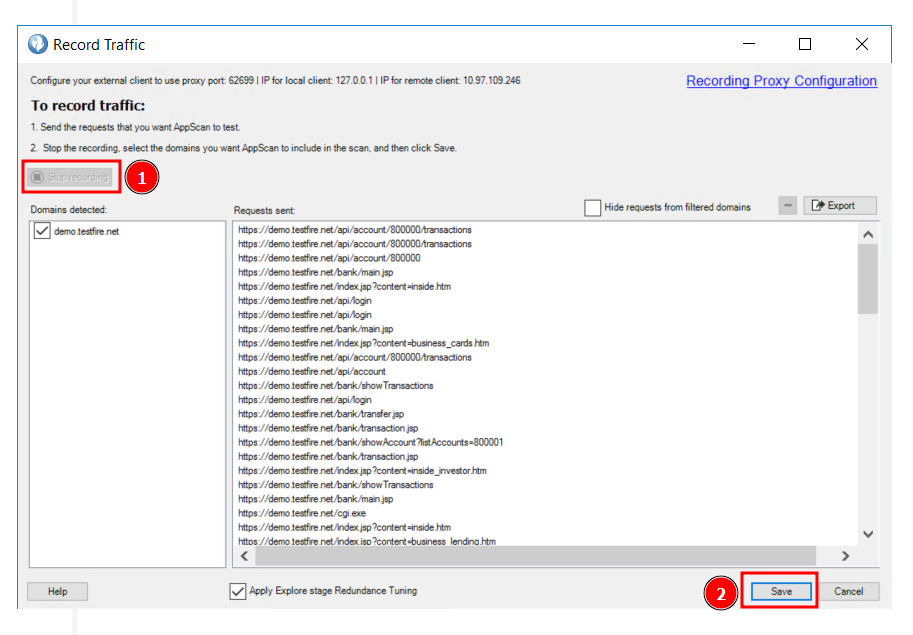
References
https://github.com/IAmRoot0/Multi-Request-Repeater/tree/main